engineering & technology publications
ISSN 1759-3433
PROCEEDINGS OF THE SIXTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURES TECHNOLOGY
Analytical Investigations of the Effects of Tension Slab Reinforcement in Cantilever Beams
Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering -– Mataria, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt
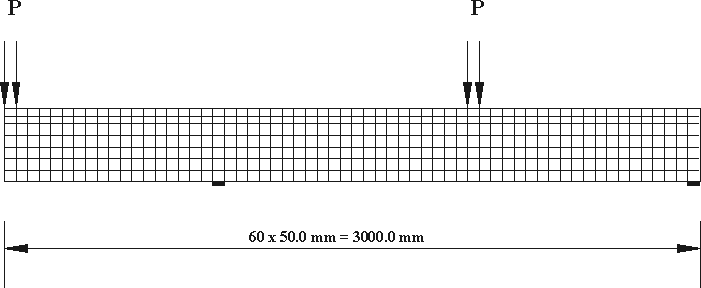
In this paper, an analytical investigation of the behaviour of T-shaped beams under gravity loads is presented. The study involved performing rigorous nonlinear finite element analyses of the beams. Several parameters are considered in the investigation. These parameters include the single and/or combined effects of the flange width, slab reinforcement, shear reinforcement ratio, beam tension reinforcement ratio, boundary conditions and loading pattern. The nonlinear finite element analysis program used in this study is that developed by the author [1] and is used for analyzing reinforced concrete structures in three dimensional space. Figure 114.1 shows the mesh discretization along the length of the beam.
The study concluded the following:
- The reinforcement in the tension slab can significantly increase the beam's
strength due to the joint action between them under gravity loads. In cases as
those studied in this paper, the beam's capacity can be increased by as much as
50% of the capacity if the slab reinforcement were to be neglected.
- Due to the observed over-strength, the mode of failure of the beam can shift
from a ductile mode initiated by yielding of the tension reinforcement to a brittle
mode initiated by either failure of the concrete compression block or by shear
failure. This effect should be definitely taken into account in case beam over-strength is
to be considered in design.
- Slab continuity in the longitudinal direction did not affect the ultimate capacity of the cantilever however, can significantly influence the deflections possibly, under other loading conditions.
- 1
- Emara, M.B. and Hosny, H.M. (1994), Program & User Manual, 'Asmbly3d', A 3-Dimensional Simplified Module of: "Assembly (Emara 1991-1994): A Nonlinear 3-D FE Analysis Program for RC Structures", ©M.B. Emara, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt.
purchase the full-text of this paper (price £20)
go to the previous paper
go to the next paper
return to the table of contents
return to the book description
purchase this book (price £125 +P&P)